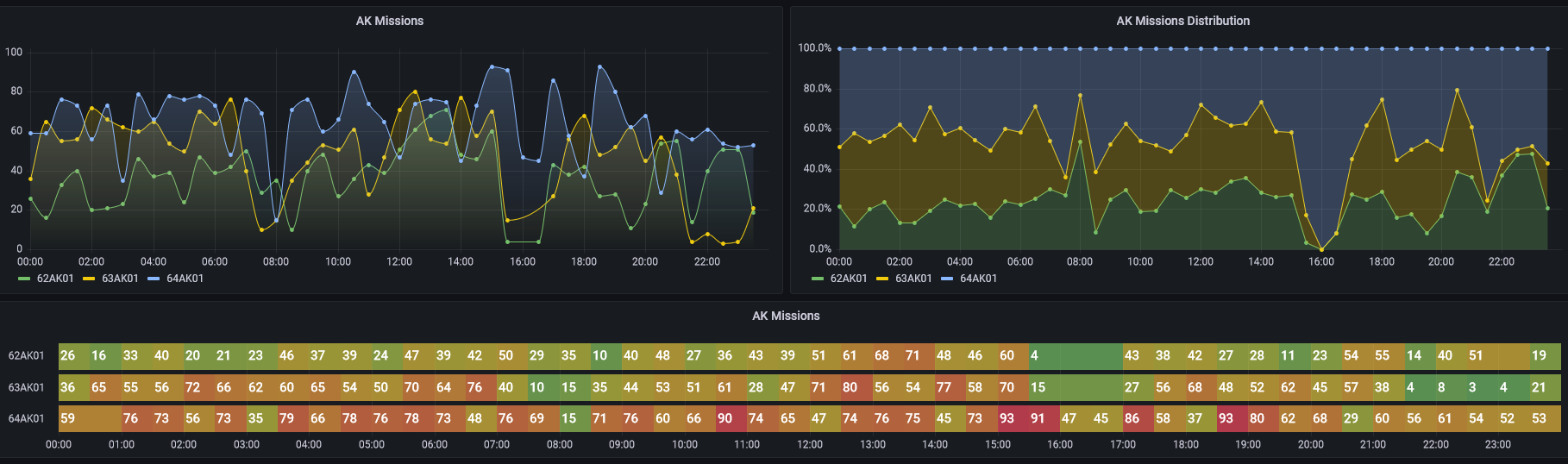
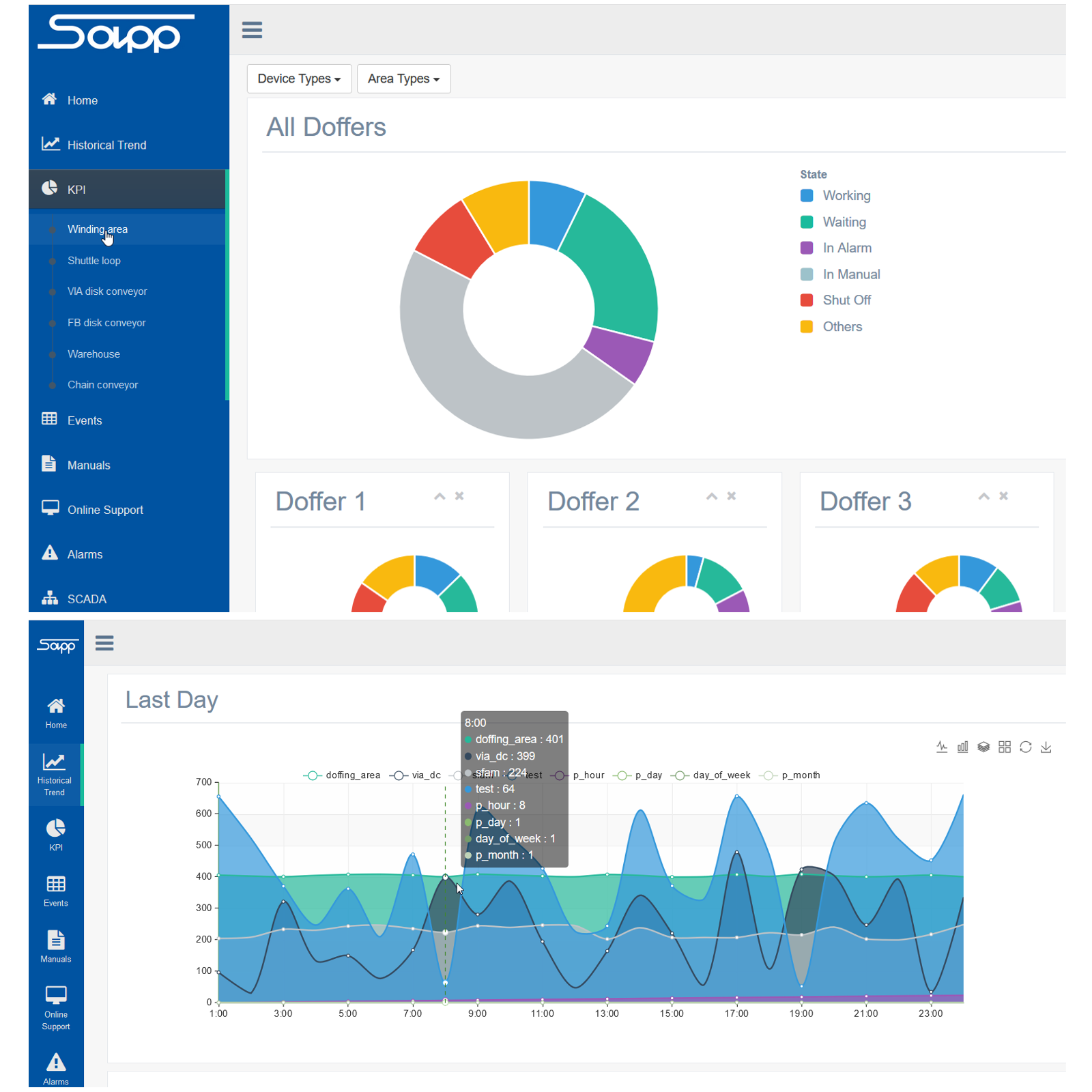
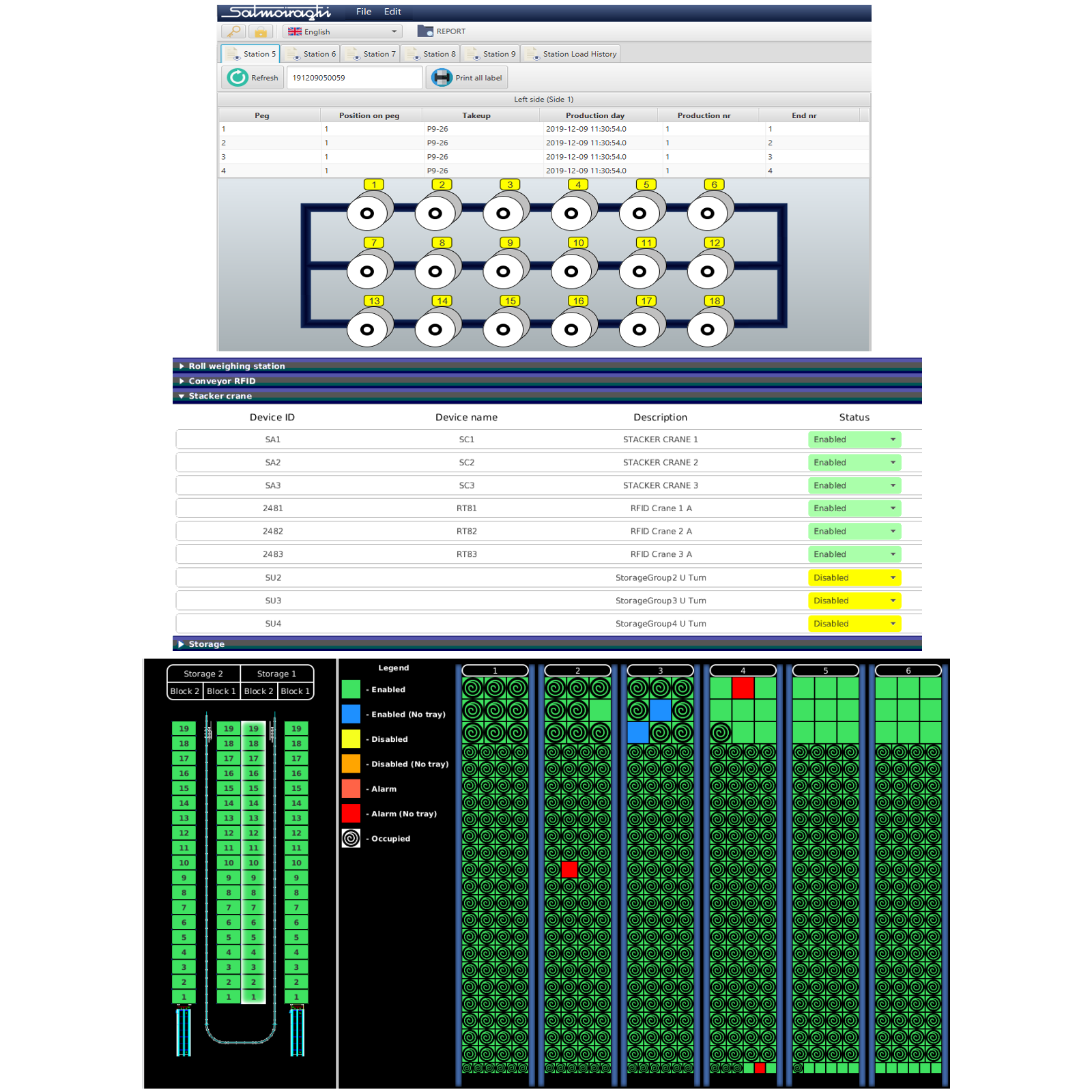
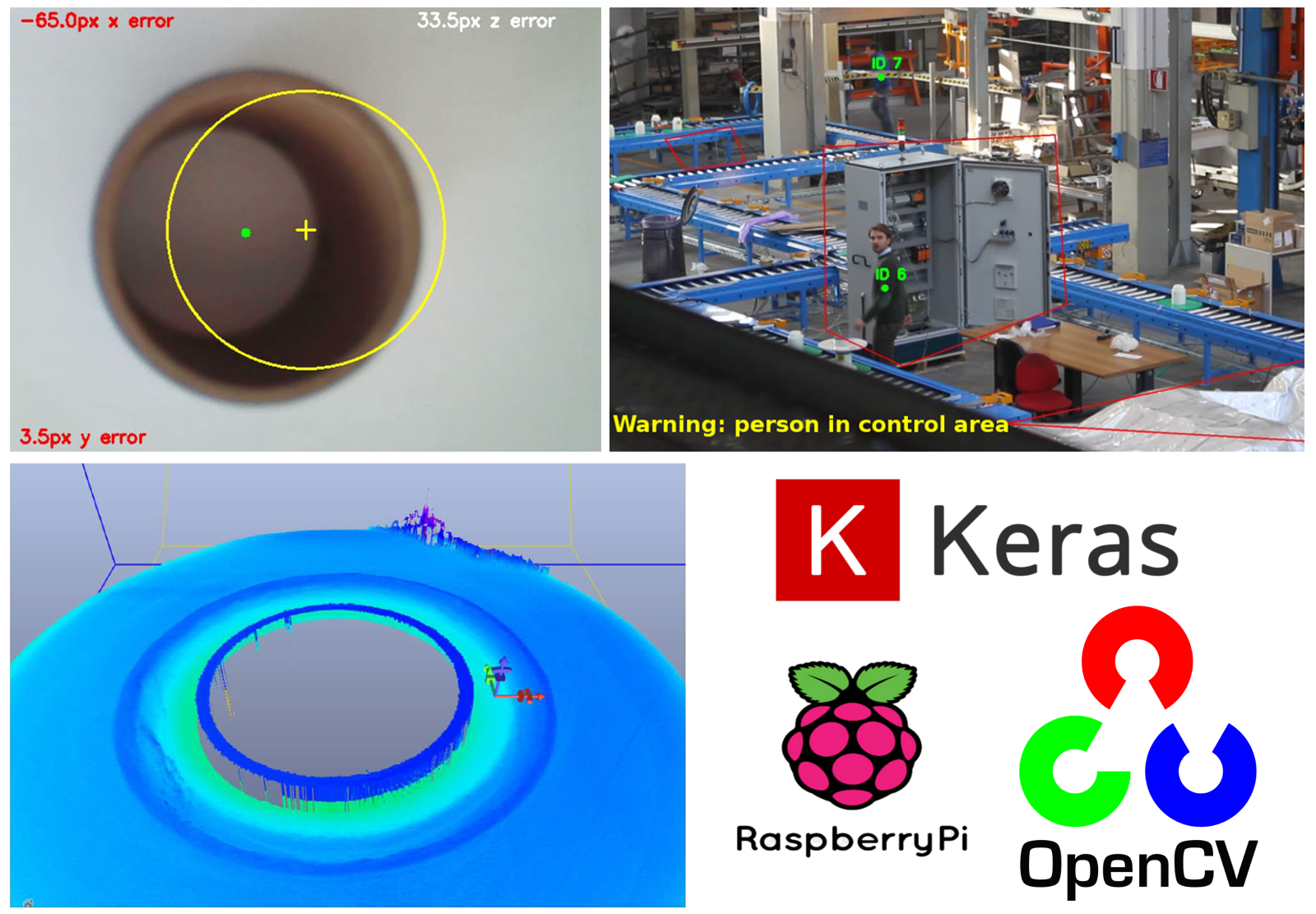
MindSphere World Italia membership
MindSphere World•July 2018 - Ongoing
Topics: Building and developing IoT ecosystems; Support in developing and improving technical solutions and in tapping new markets in the digital economy; Contact with public and private institutions for shaping public opinion and making decisions
Automatic machines safety and standards course
Sick AG•Nov 2022 - Feb 2023
Topics:
- Machinery directive and principles of safety
- Risk evaluation analysis and EN ISO 12100
- Functional safety and EN ISO 13849-1
- Standards for Robots and systems EN ISO 10218-1, EN ISO 10218-2, ISO/TS 15066
- Standards for Industrial Trucks and systems EN ISO 3691-4
Speaker at SIMAI (Società Italiana di Matematica Applicata all'Industria) Biannual Congress
SIMAI•September 2016
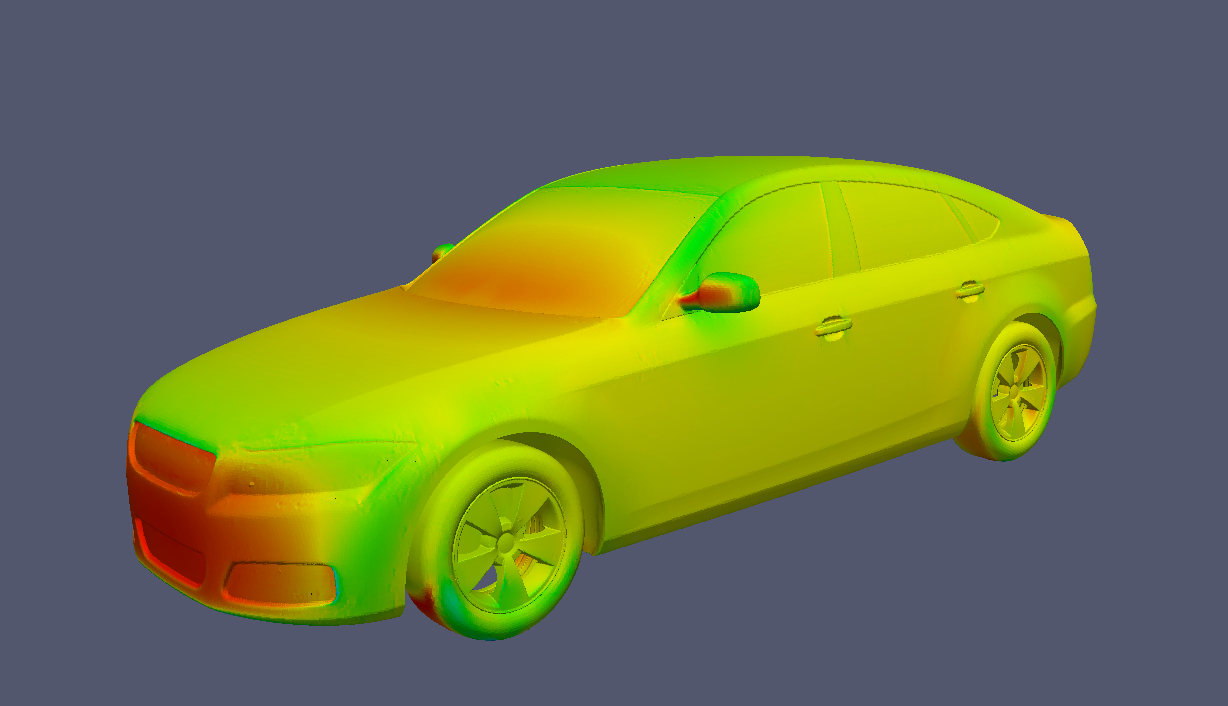
Title: Reduced Order Methods for Automotive and Nautical applications
Speaker at MoRePaS (Model Reduction for Parametrized Systems) 2015
MoRePas•October 2015
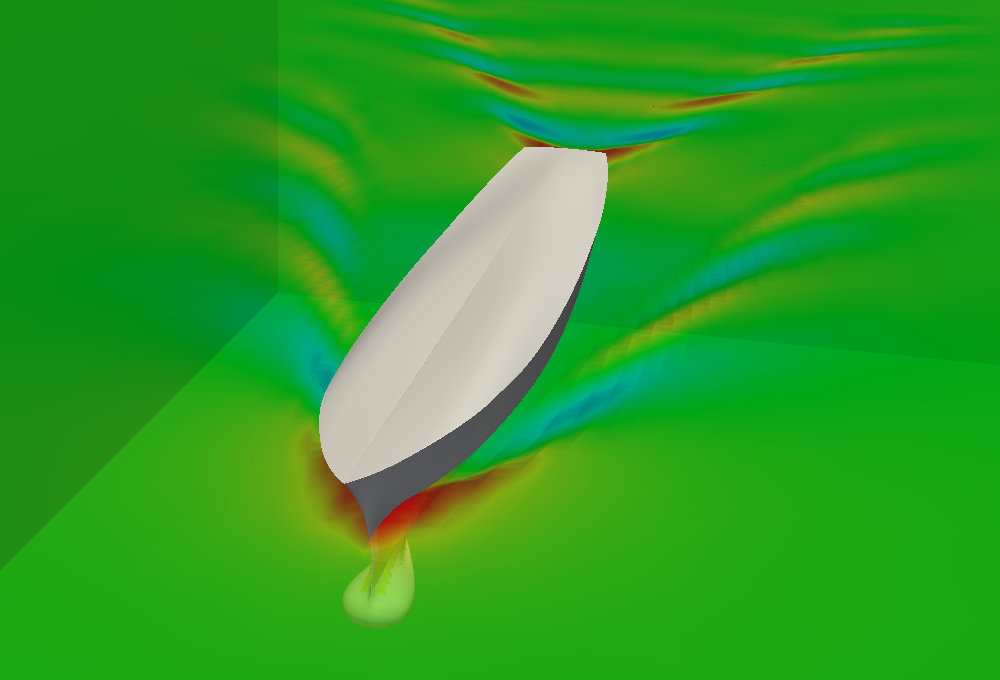
Title: Isogeometric analysis based reduced order modelling for incompressible viscous flows in parametrized shapes: applications to underwater shape design
Dobbiaco Summer School
Dobbiaco•June 2015
Topics: Innovative concepts for complexity reduction in numerical PDEs: nonlinear approximation, sparsity, adaptivity, model reduction
COST EU-MORNET meeeting on Reduced Order Methods
COST and EU-MORNET•February 2015
Topics: Innovative concepts for complexity reduction in numerical PDEs: nonlinear approximation, sparsity, adaptivity, model reduction
INDAM Young Scientists Seminars Series on Reduced Order Modeling
SISSA•October 2014
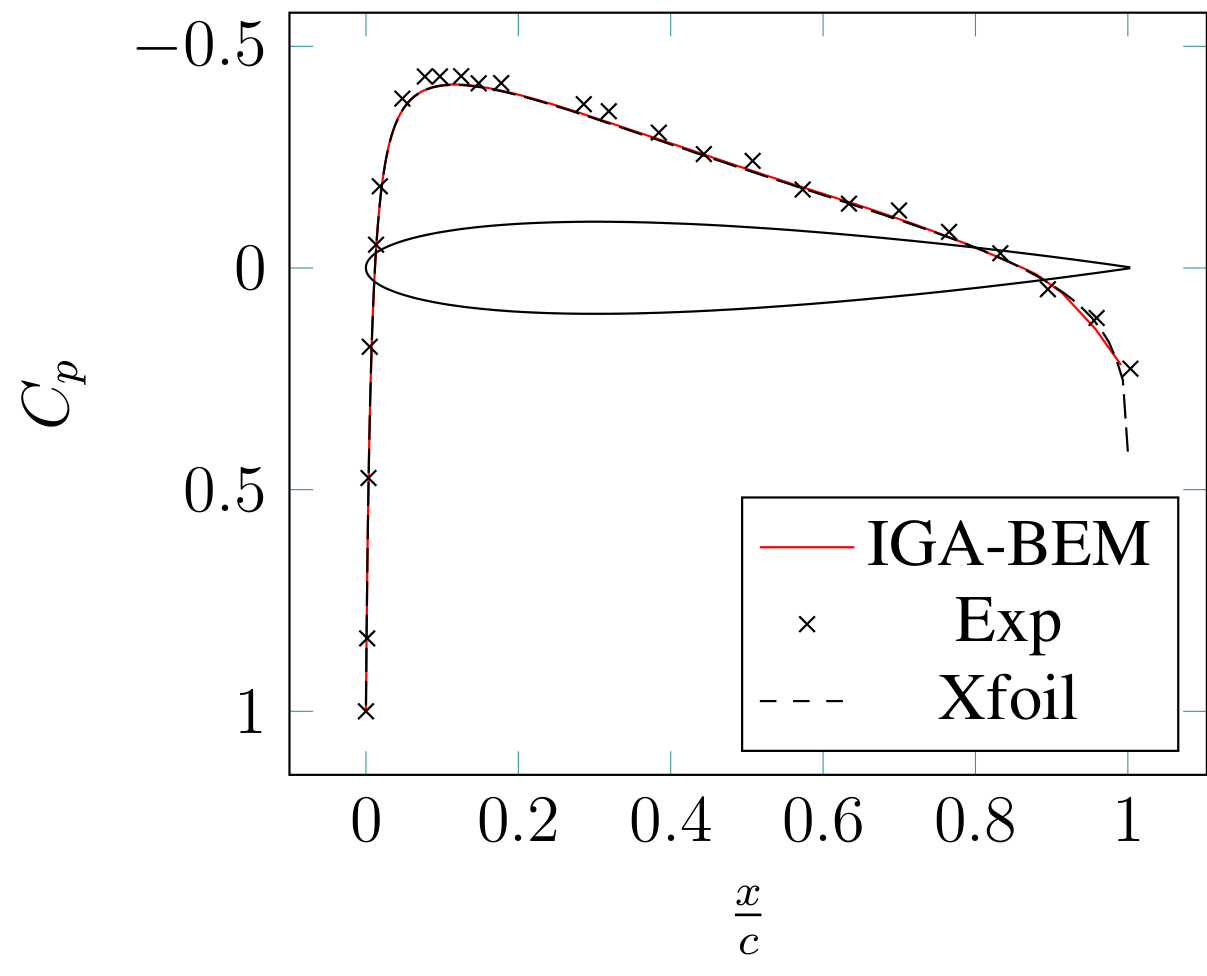
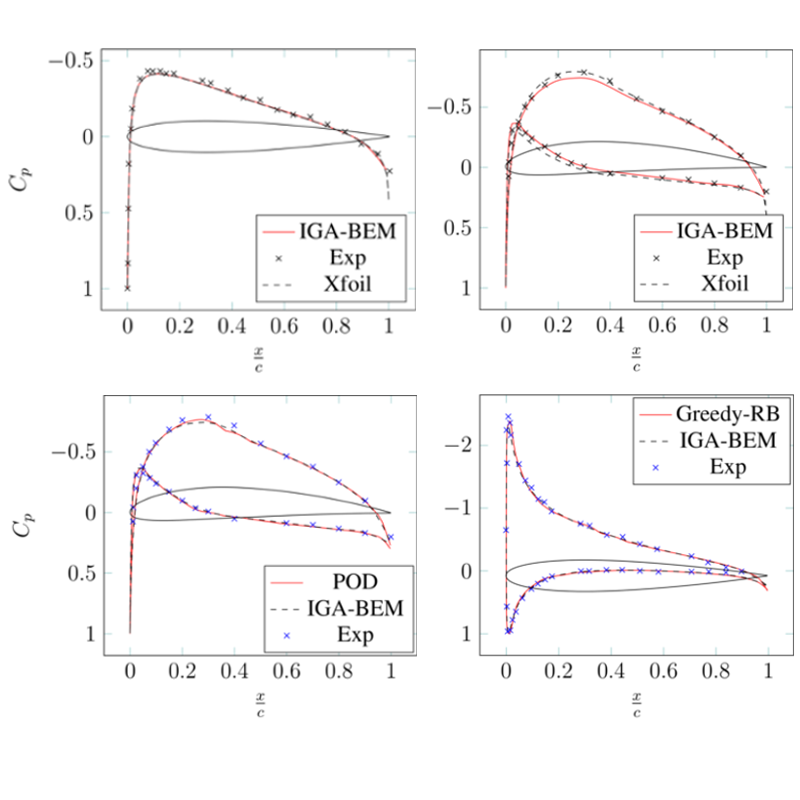
Topics: Reduced Basis Isogeometric Boundary Element Methods for the real-time simulation of flows around parametrized NACA airfoils
Master in High Performance Computing
(pilot courses)
ICTP and SISSA•September 2013 - December 2013
Topics: Scientific Programming Environments and Object Oriented Programming